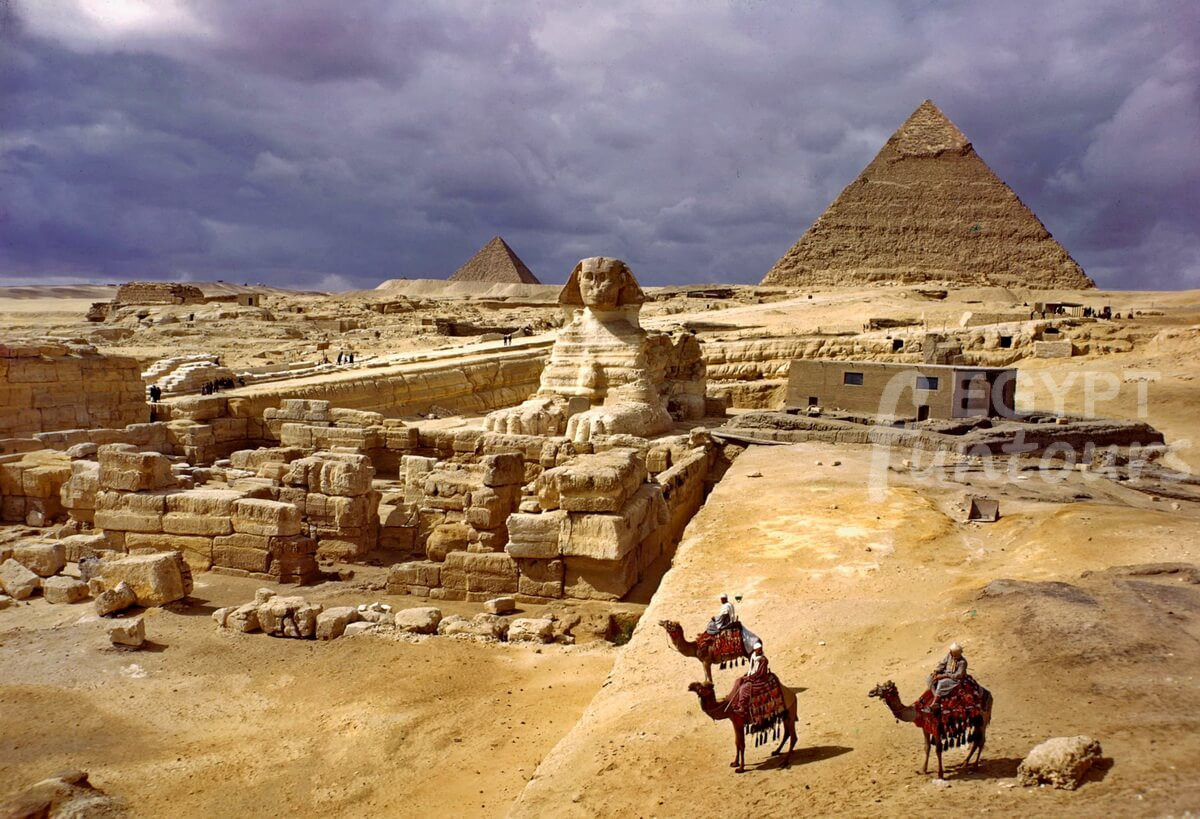
Are you ready to delve into a world of mystery, symbolism, and awe-inspiring achievements? The ancient Egyptian pyramids aren’t just history; they are a living story of ambition and ingenuity, and they continue to intrigue us to this day. Join us at Egypt Fun Tours as we take you on a journey through the most captivating ancient Egyptian pyramids facts that illuminate these timeless wonders.
Key Facts to Start Your Journey
Before we dive deep, here are the essential facts you need to know:
- What were they? Simply put, they were grand, monumental tombs for the pharaohs and their consorts.
- How many? We’ve discovered over 130 pyramids so far, scattered across Egypt.
- Who built them? This is a popular question! Tens of thousands of skilled, paid, and well-fed laborers built them—not slaves, as many believe.
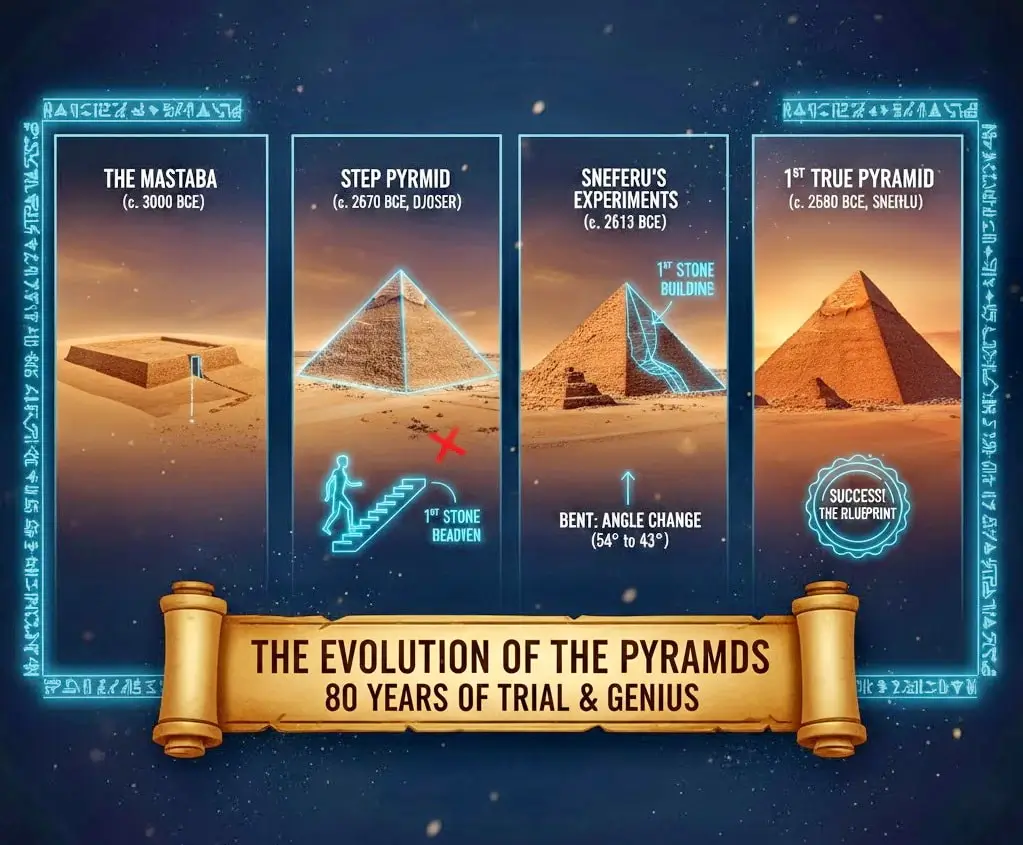
- Which is the oldest? That honor goes to the Step Pyramid of Djoser in Saqqara (built c. 2630 BC).
- Which is the biggest? The one and only Great Pyramid of Khufu in Giza.
- Why that shape? We believe it symbolized a “stairway to heaven,” allowing the pharaoh’s soul to ascend to the gods.