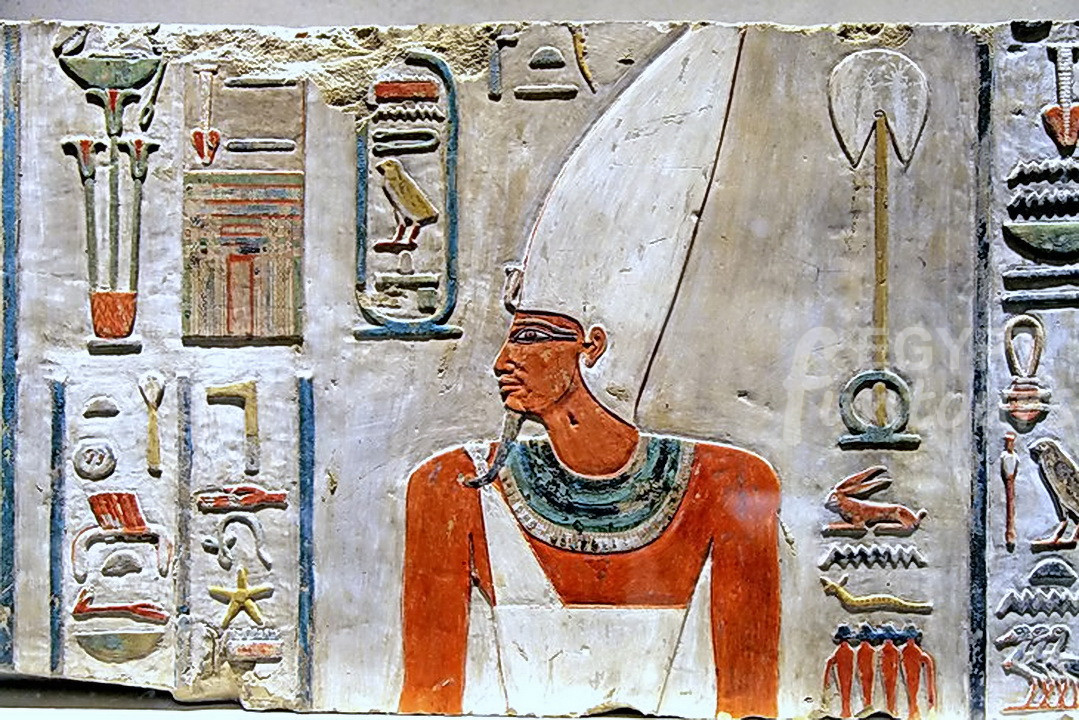
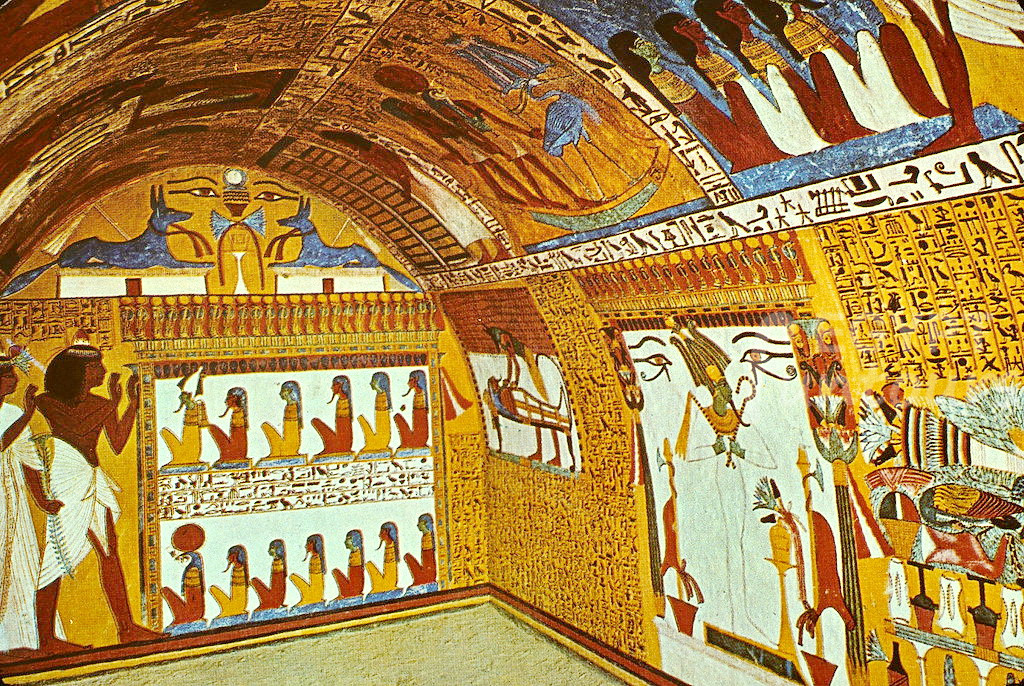
What Was Inside an Ancient Egyptian Tomb?

Once an ancient Egyptian tomb was sealed, it became a locked “time capsule” containing all the “eternal equipment” the deceased needed for the afterlife. This included:
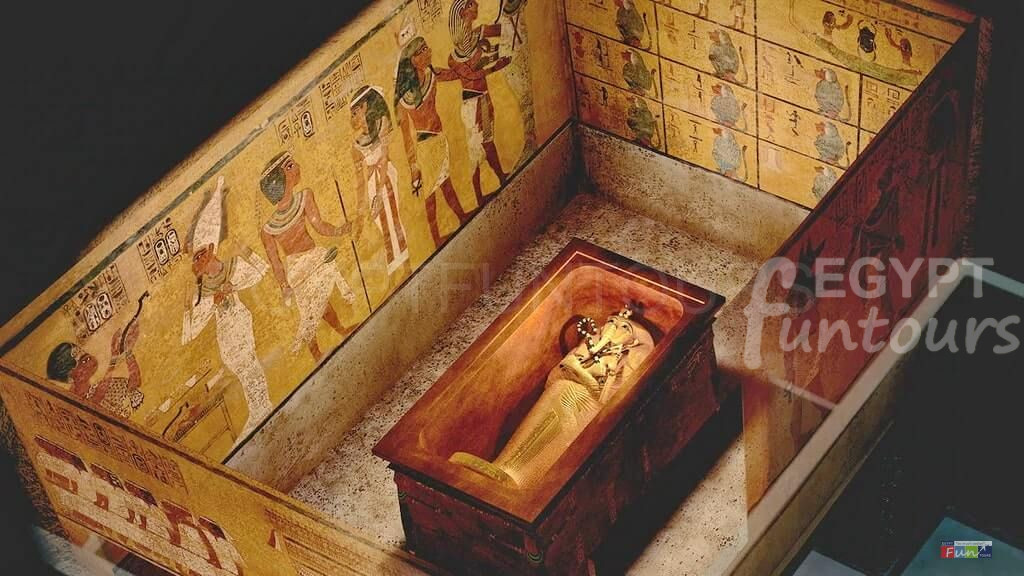
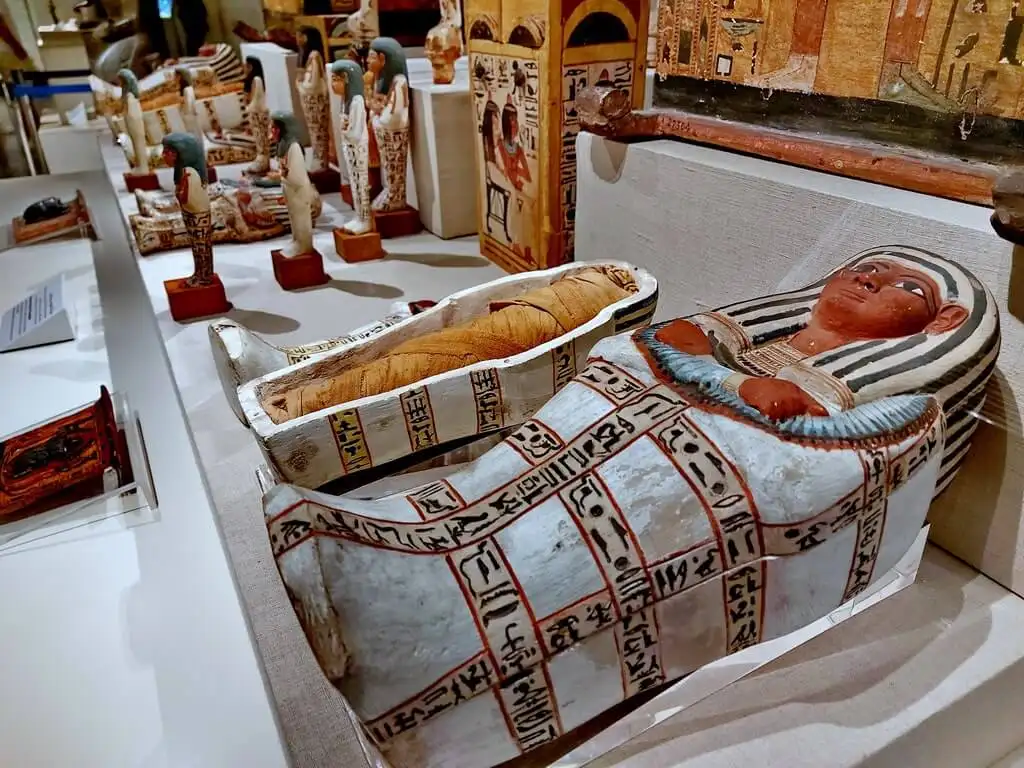
The Mummy: This was the primary “vehicle” for the soul, a preserved body for the Ka and Ba to return to.
The Coffin & Sarcophagus: These were the nested layers of magical and physical protection. A pharaoh might have multiple wooden or gold coffins placed inside a massive, stone sarcophagus.
Learn More: A pharaoh’s outer coffin was a magical tool. Read all about it in our Guide to the Ancient Egyptian Sarcophagus.
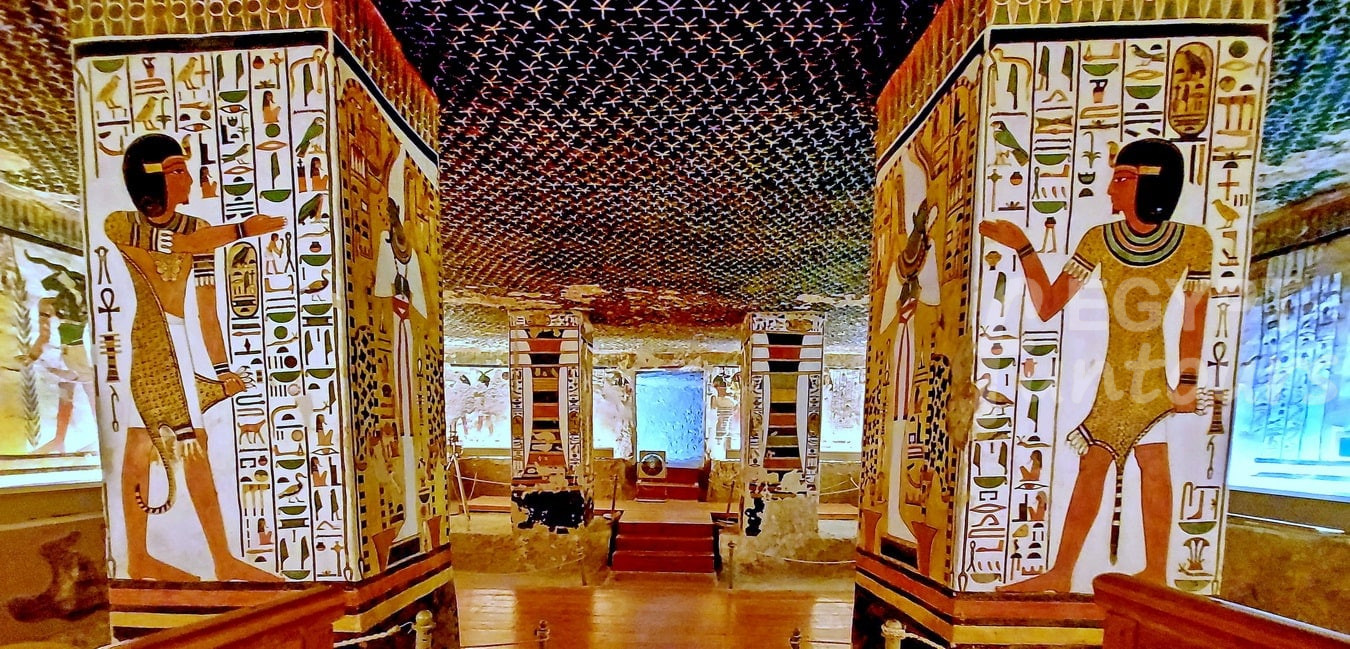
Funerary Objects: This was all the “stuff” needed to live a comfortable eternity. The most important ancient Egyptian funerary objects included:
- Canopic Jars: Four jars to hold the mummified organs.
- Shabti Figures: Small magical “servant” statues, one for every day of the year, to do the pharaoh’s work in the afterlife.
- Personal Goods: Furniture (beds, chairs, headrests), food, wine, clothing, jewelry, weapons, and even games like Senet.
See the Treasures: For a full list of these items, see our Guide to Ancient Egyptian Funerary Objects.
A 3,000-Year Quest to Defeat Death

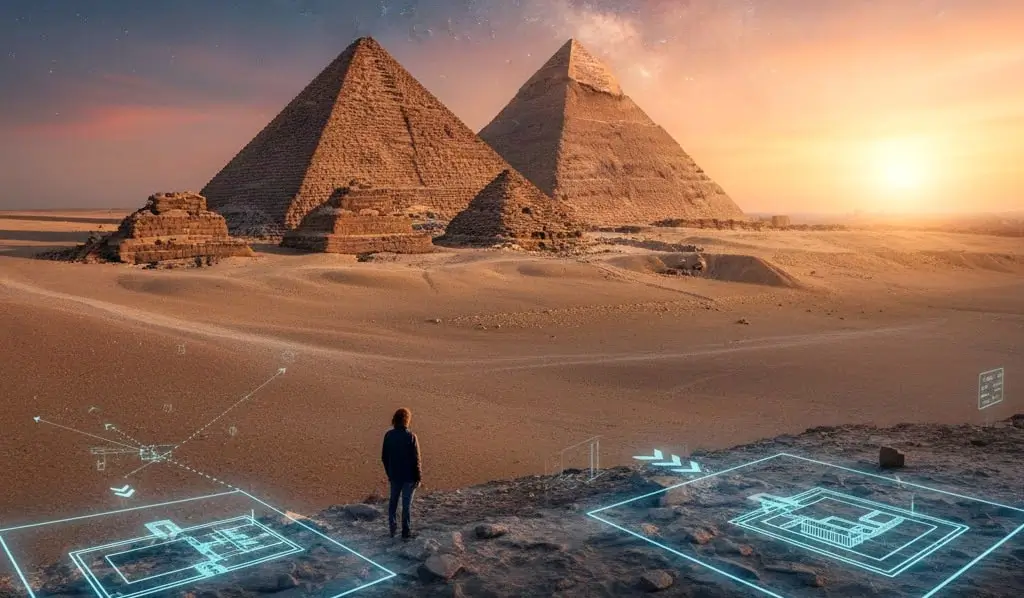
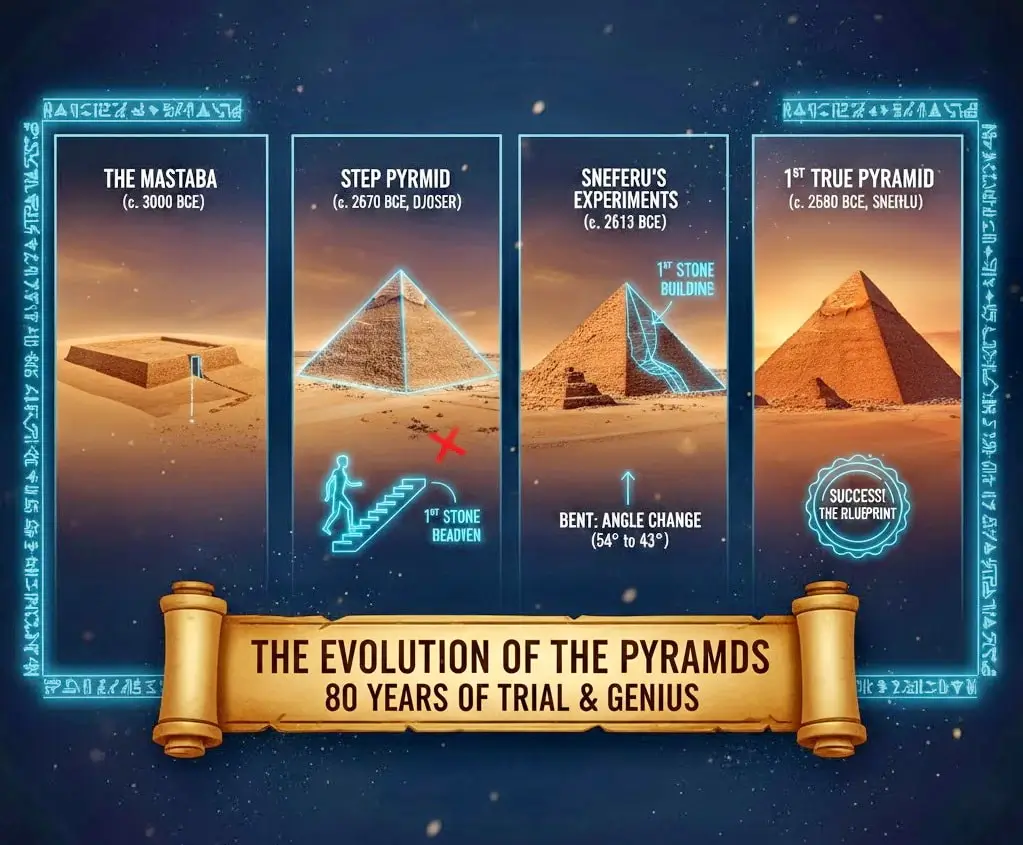
We have now traced the 3,000-year history of the ancient Egyptian tomb. We saw it evolve from a simple sandpit into a stone mastaba. Then, it transformed into a “stairway to heaven” (the Step Pyramid), endured brilliant failures (the Bent Pyramid), and achieved stone perfection (the Great Pyramid). Finally, we saw it vanish into the secret cliffs of the Valley of the Kings.
Throughout this journey, the tomb remained the civilization’s greatest focus. It served as the primary arena for their best artists, engineers, and theologians. Ultimately, ancient Egyptian tombs were not a morbid obsession with death. Instead, they stand as a powerful, 3,000-year-long celebration of life and an unshakeable, practical belief in eternity.
FAQs About Ancient Egyptian Tombs
Here are the quick, direct answers to the most common questions about ancient Egyptian tombs.
Q: What is the main purpose of an ancient Egyptian tomb?
A: It had three main jobs: to protect the mummy, to provide a permanent home for the soul (Ka), and to store all the food, magic, and furniture (funerary objects) that the deceased needed for the afterlife.
Q: Why did the Egyptians stop building pyramids?
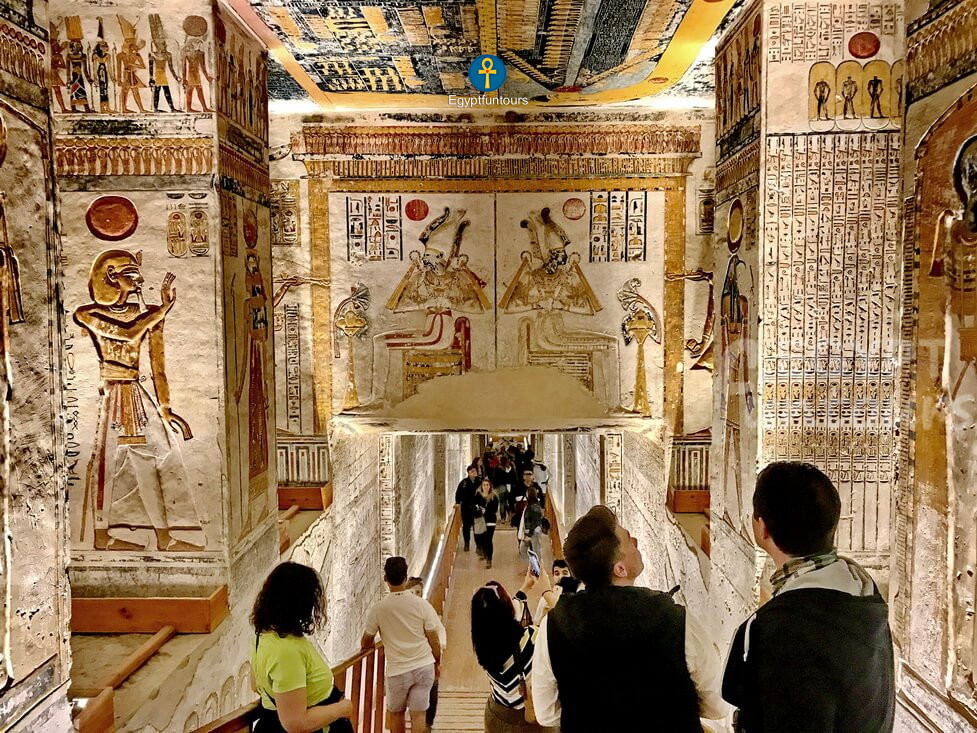
A: Because they were all robbed. The pyramid’s massive, obvious shape made it an impossible-to-miss target for tomb robbers. So, they switched to secret, hidden, rock-cut tombs (like in the Valley of the Kings) for better security.
Q: What is the most famous tomb in Egypt?
A: The Tomb of Tutankhamun (KV62). This is not because he was a great king, but because it was discovered almost completely intact in 1922, giving us a glimpse of real royal treasure.
Q: What is the difference between a tomb and a mortuary temple?
A: The tomb (like a pyramid or KV62) held the physical mummy. The mortuary temple (like Hatshepsut’s) was a separate “church,” often miles away, where priests performed daily rituals to “feed” the king’s spirit.
Q: Can you go inside the tombs?
A: Yes. Visitors to Egypt can enter many ancient Egyptian tombs. This includes the Pyramids at Giza and a rotating selection of tombs in the Valley of the Kings and the Tombs of the Nobles.