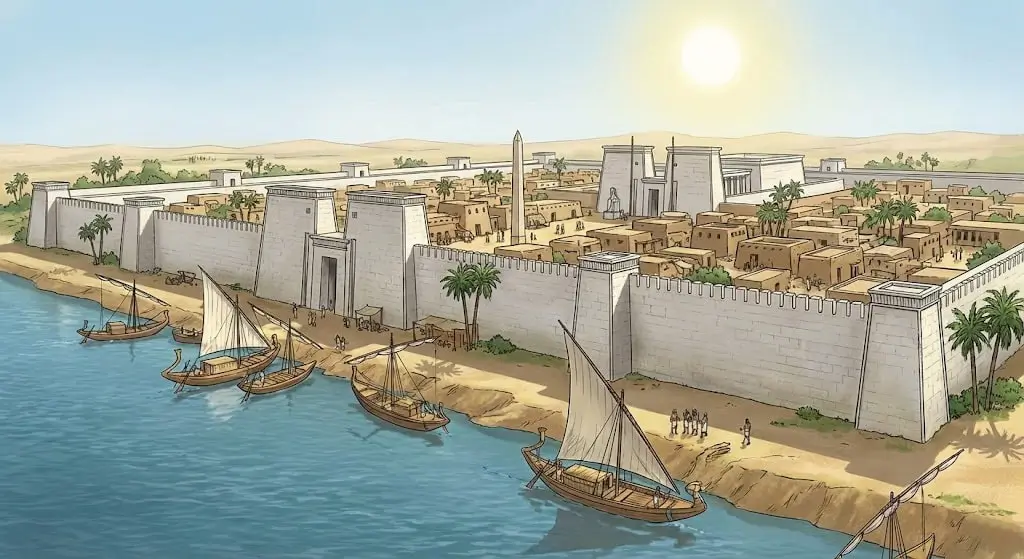
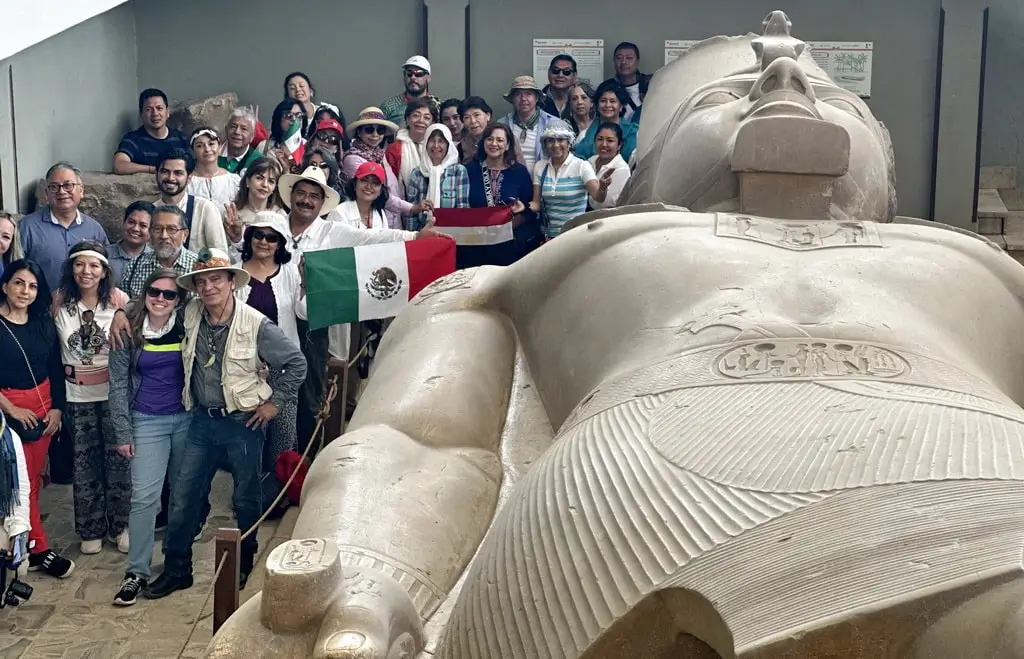
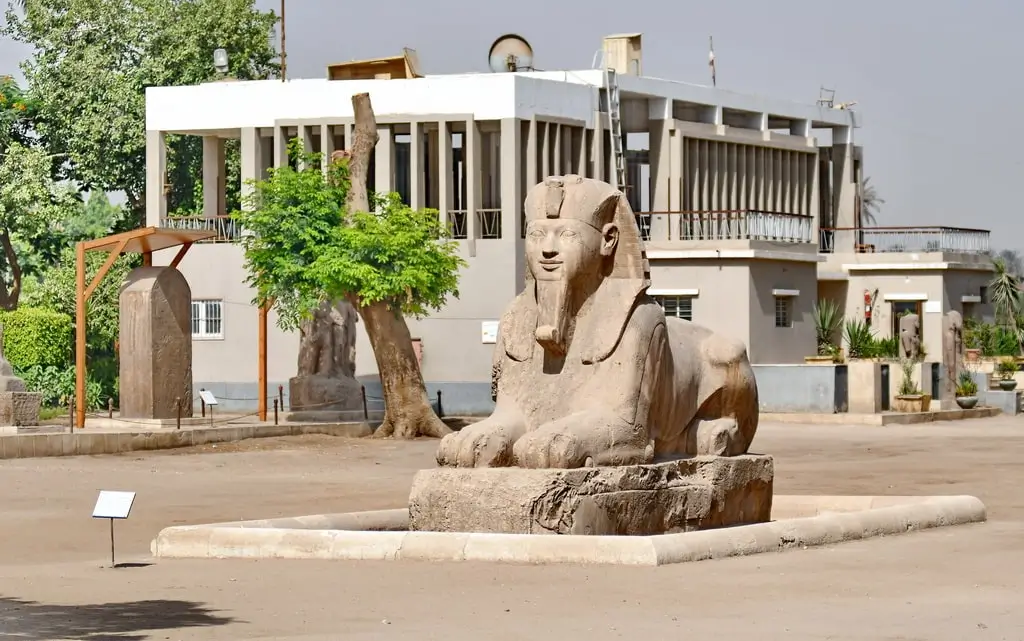
If you visit Luxor (ancient Thebes), you see massive temples standing proudly against the sky. If you visit Memphis, you see palm trees. This is the great tragedy of Egyptian archaeology. Memphis was the capital of Ancient Egypt for eight consecutive dynasties. It was the New York, the London, and the Vatican of the ancient world combined.
But here is the catch.
Today, the city is almost entirely gone. While the stone temples of the south survived, the mud-brick palaces of Memphis crumbled. Furthermore, when the Arabs conquered Egypt in the 7th century AD, they used Memphis as a quarry. They dismantled its white walls to build the new capital of Cairo. Consequently, Memphis did not just die. It was cannibalized.
The Brain of Egypt
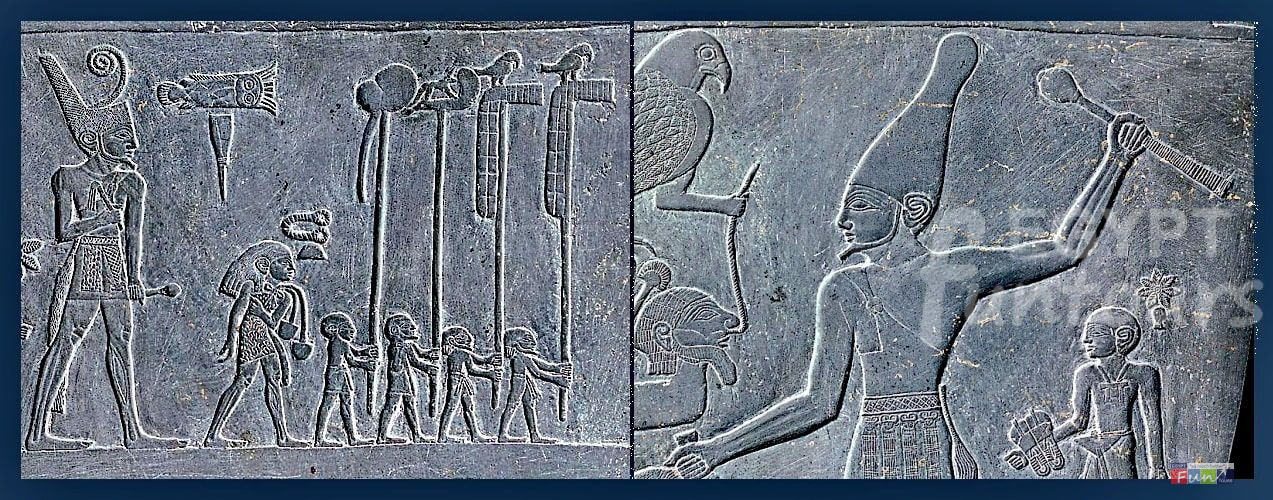

To understand Ancient Egypt, you must understand the balance between its two great cities.
- Thebes (Luxor): This was the religious heart with the burial places of the New Kingdom Kings.
- Memphis: This was the brain. It was where the kings actually lived and ruled.
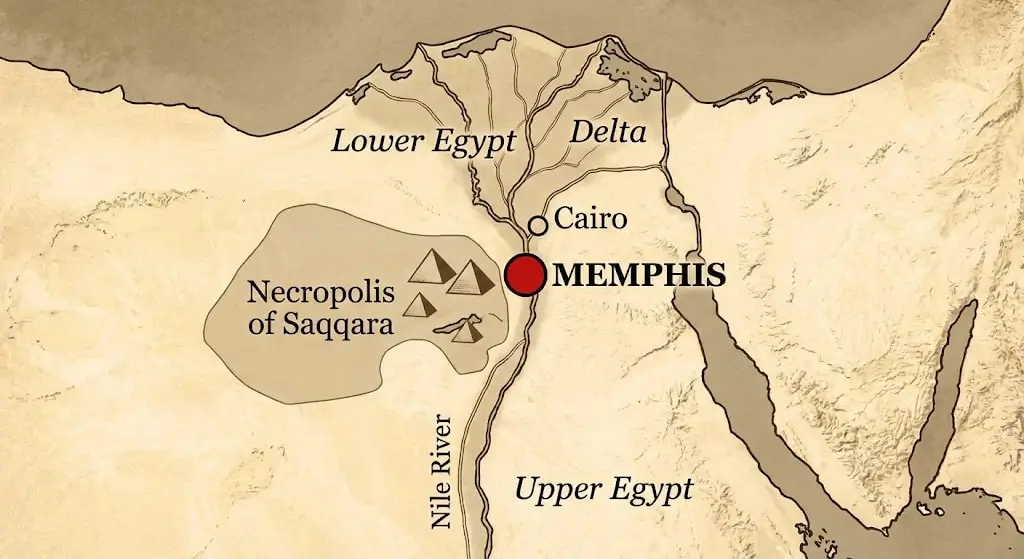
Founded by King Menes around 3100 BC, Memphis was built for a specific purpose: Control. It sits exactly at the apex of the Nile Delta, where the river splits. From this strategic choke point, the Pharaoh could command both the Upper Nile valley and the Mediterranean coast.
- The Name: The Egyptians called it Ineb-Hedj, meaning “The White Walls,” referring to the gleaming limestone fortress that surrounded it. Later, it was named Men-nefer (“Enduring and Beautiful”), which the Greeks corrupted into “Memphis.”
- The God: It was the seat of Ptah, the god of craftsmen who spoke the world into existence.
In this guide, we reconstruct the lost city. We explore the ruins of the Temple of Ptah, marvel at the colossal fallen statue of Ramesses II, and descend into the mysteries of the Serapeum, where the ancients buried bulls like kings.