6. Osiris, the “Justice God”
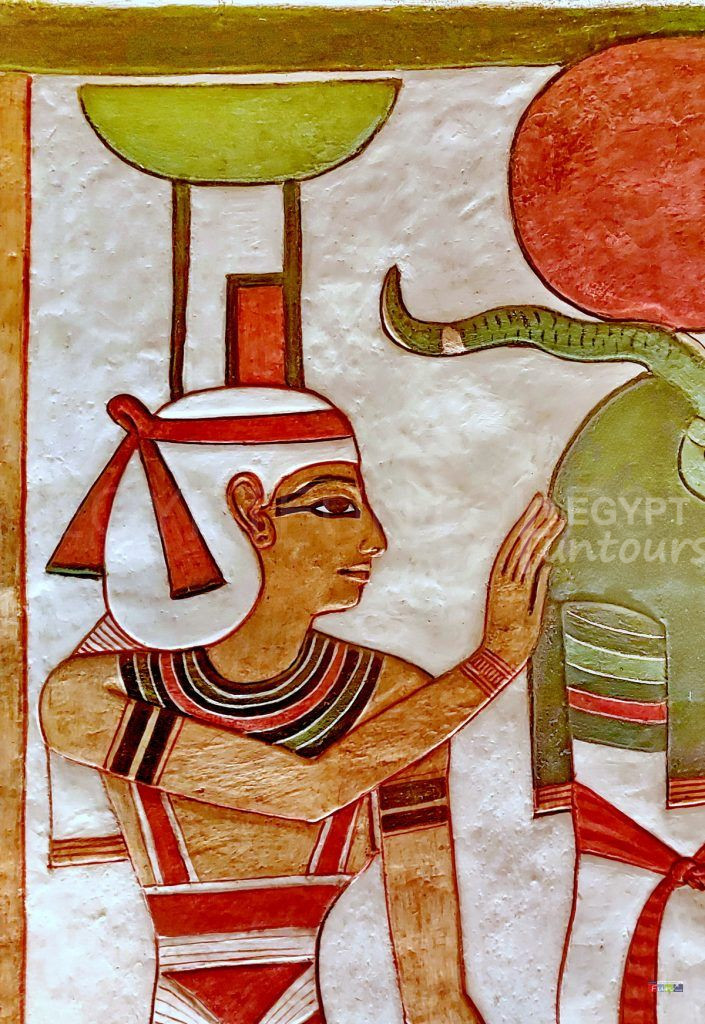
Osiris is the great-grandson of Amun and the king of the Underworld. He is one of the five primordial gods and one of the early gods of creation.
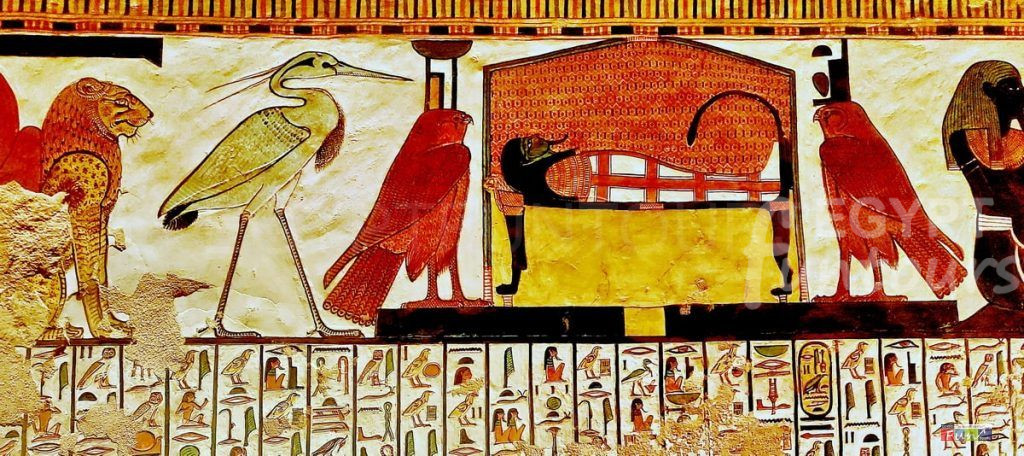
Osiris was a fertility god who gained fame, popularity, and influence as a result of the Osiris Myth, in which he was killed by his evil brother Set, “God of the Desert,” and then resurrected by his sister-wife Isis, “Goddess of Motherhood and Healing,” and Horus the Elder, before descending to the underworld and becoming a lord and judge of the dead.
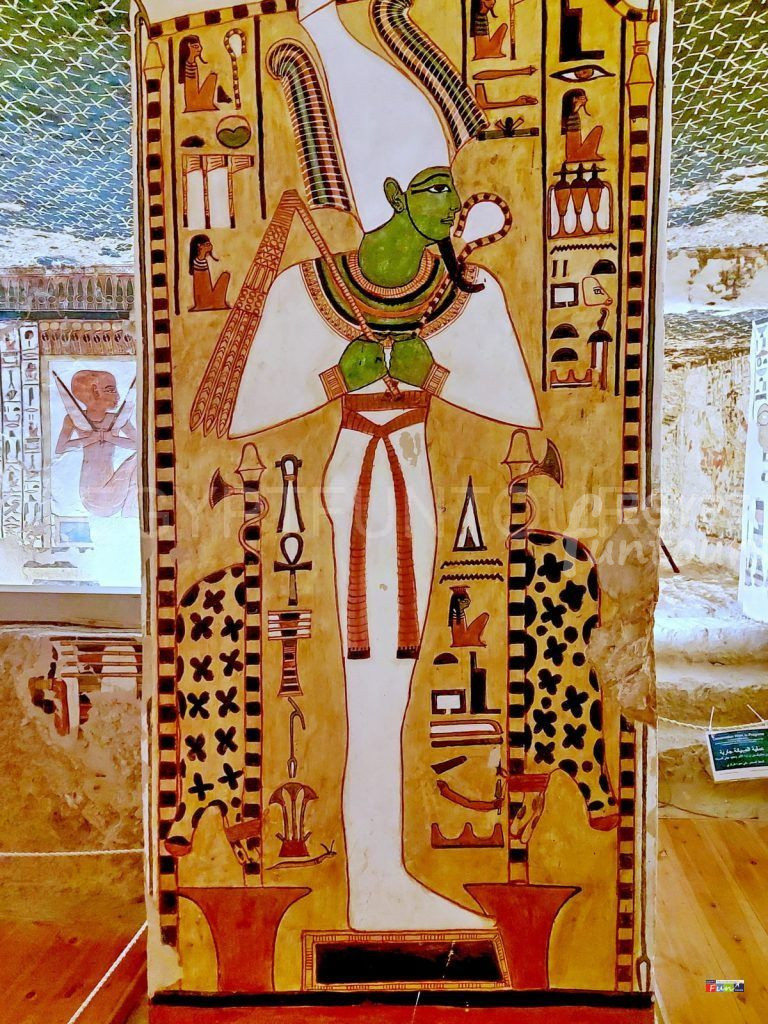
He is the primary judge in the afterlife’s Hall of Truth, weighing the souls of the deceased against a white feather of the goddess Maat, the “Goddess of Truth and Justice.” Osiris is generally portrayed as a mummy with green or black skin, two ostrich plumes, and a beard, wielding a crook and flail of royalty. In Abydos, many ancient Egyptians opted to be buried alongside their worship.
7. Isis, the “Mother Goddess.”

Isis, also known as Mut-Netier, “Mother of the Gods” and West-Kekau “The Great Magic,” has evolved into a super goddess with ties to nearly every element of humanity’s existence, death, and time. She was the mother of Horus, the falcon sky deity, and the wife of Osiris, the king of the underworld.
Eset, which means “Goddess of the Throne,” was her name. Due to the Osiris story and her real compassion for other gods and humanity when she appeared to them after death to guide them to paradise, she became the most powerful and famous Egyptian goddess.
She had a tail and a throne on her head, and she was occasionally seen breastfeeding her son Horus. She had a vast, strong cult that was adored in every corner of the globe, from Britain through Europe, Greece, and Rome, to Asia.
8. Horus, the “God of the Sky.”
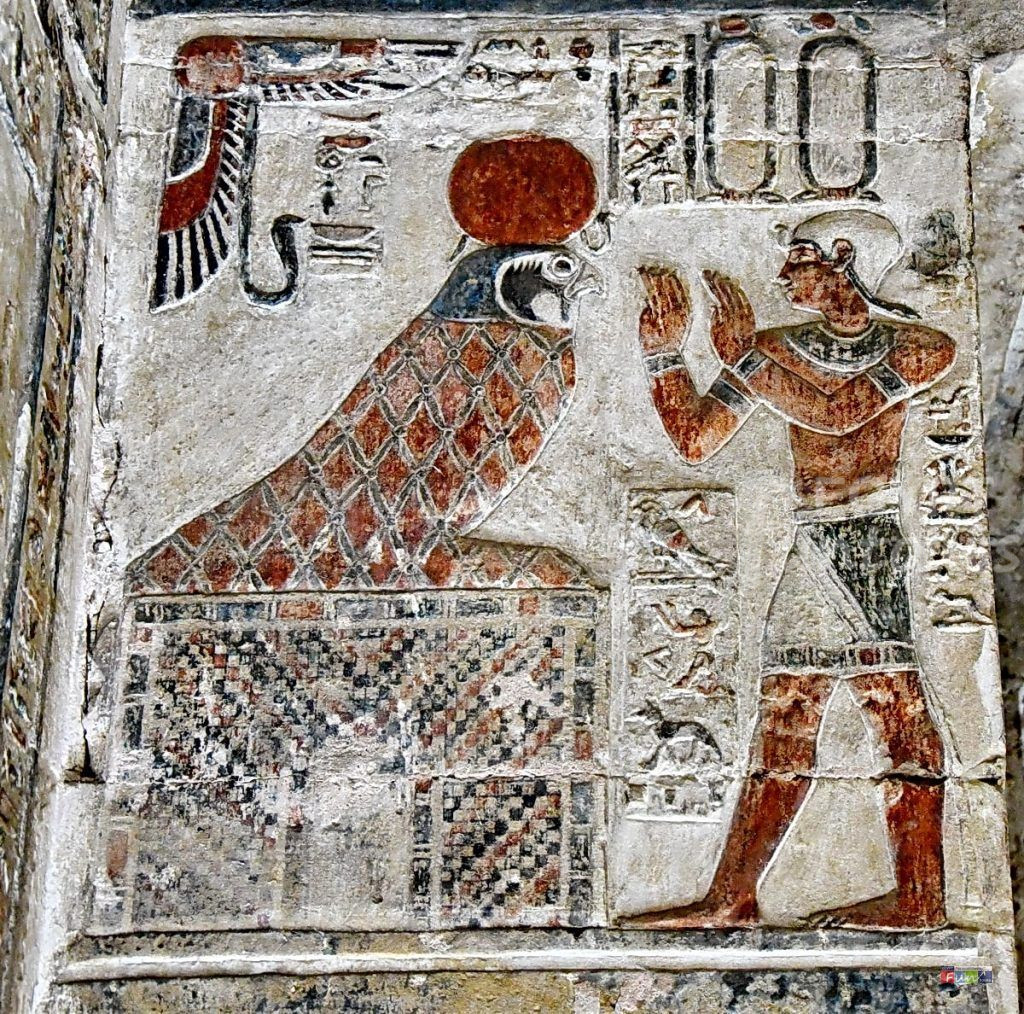

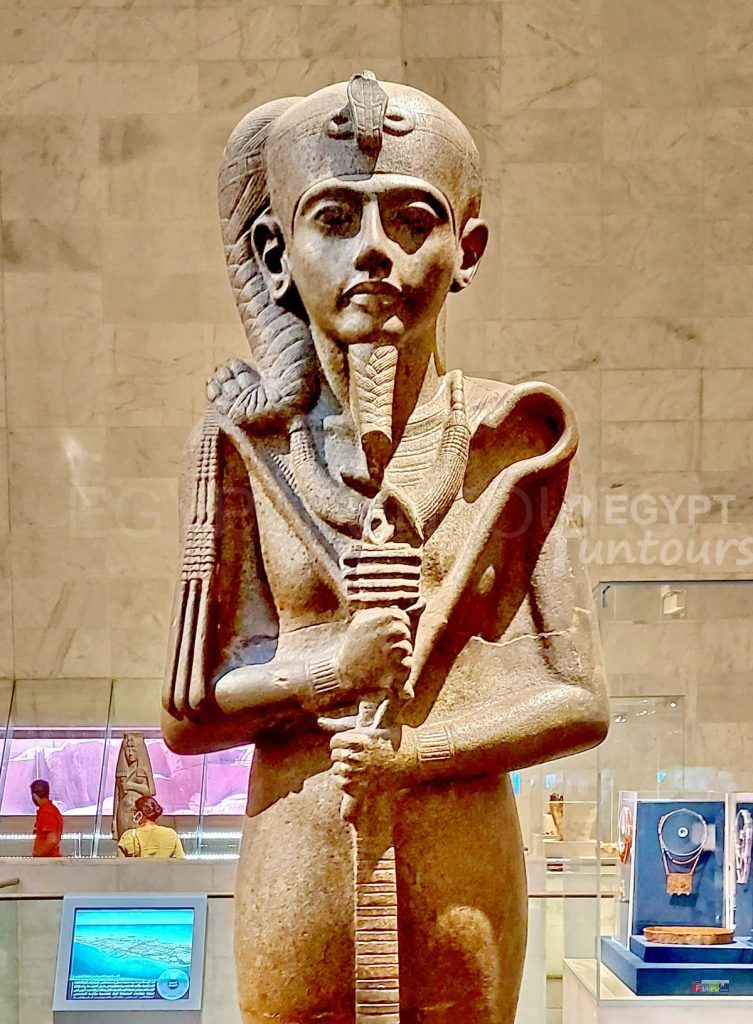
The son of Osiris, the king of the underworld, and Isis, the goddess of maternity and healing, Horus is a mythical sky god. Horus is an avian god associated with the sky, the sun, and the divine force of the skies. Because of the Osiris Myth, in which he faces and destroys his wicked uncle, he is highly renowned and well-known among the Egyptian kings as a symbol of triumph and order, and all the kings thought that they were the embodiment of Horus in life and his father Osiris in death.
Set out to avenge his father and restore Egypt’s rule and tranquility. His emblem is the Hawk, as well as the Wadjet Eye of Horus, which he sacrificed to save his father. Many people mistake him for Hours the ELDER, an early deity of creation. He generally appears as a man with the head of a big hawk or falcon and assumes the form of a giant hawk or falcon.
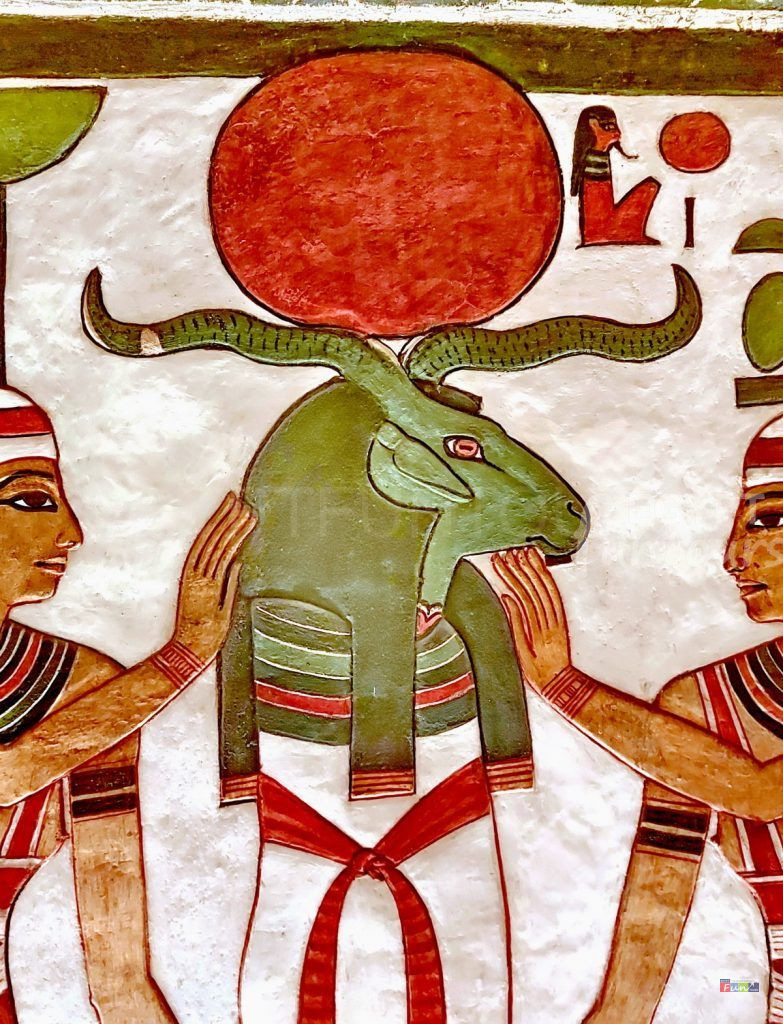
9. Set “God of Deception.”
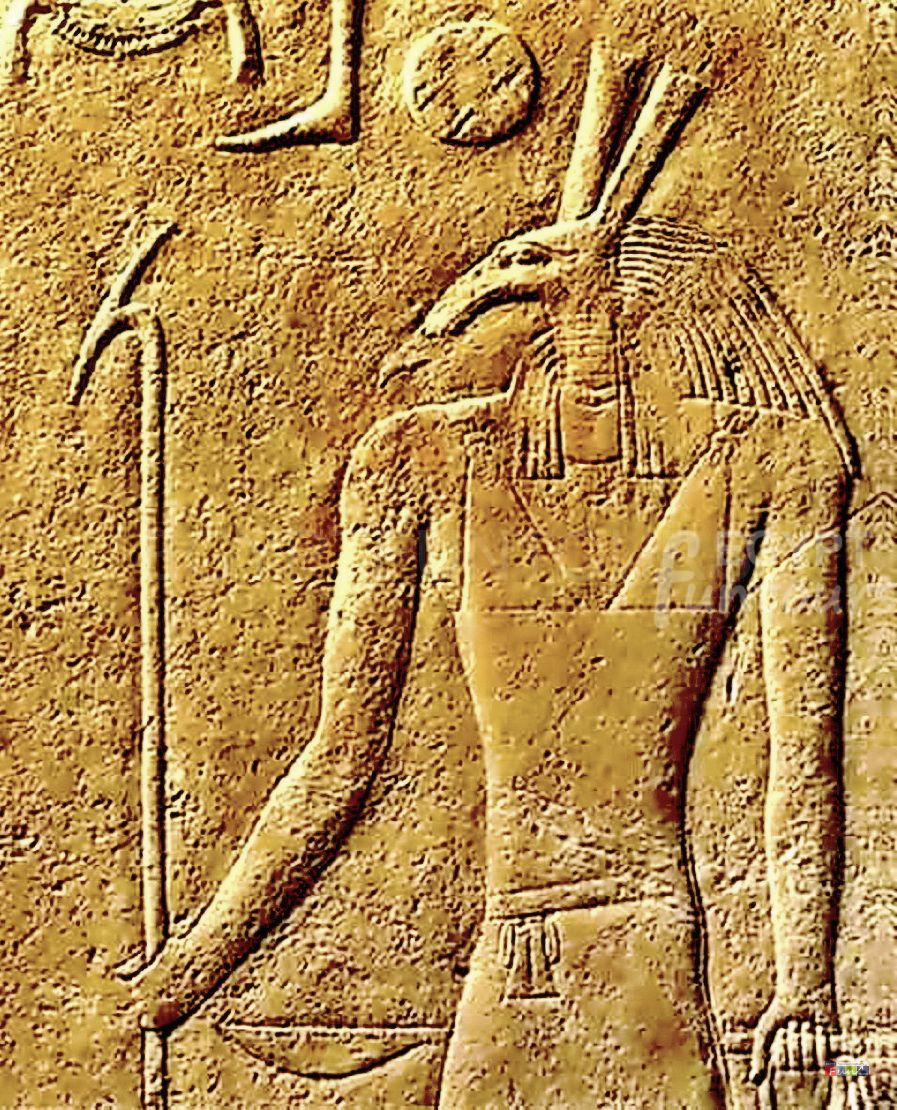

Set was a god of chaos, disease, and war. He had a monstrous head and a tail. People also called him “The Destroyer” and “the Instigator of Confusion.” People consider him a figure of evil because he assassinated his brother Osiris. After his death, Osiris became the lord of the underworld. This event brought a new era of gloom to Egypt.
Set was also a desert deity. He summoned evil winds to the Nile River to take control of the kingdom. He fought alongside Ra on his solar boat against the snake Apophis.
Set fought his nephew, the sky god Horus, for eight years. This battle took place at the site that became known as the Edfu Temple. In the end, Horus won and became King of Egypt. Set is often portrayed as a red, fox-like creature with hooves and a forked tail. He brings disasters like storms, tsunamis, and volcanoes.
10. Ma’at, the “Goddess of Balance.”
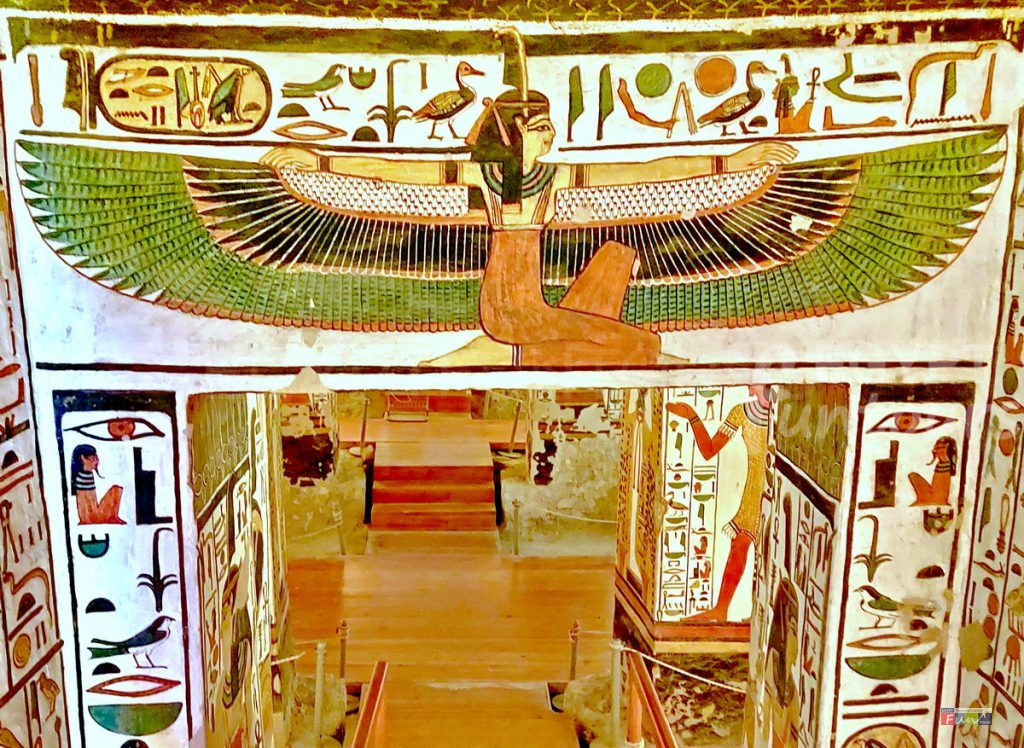

Ma’at is the goddess of justice, truth, and cosmic balance, a central figure within the ancient Egyptian pantheon. She represents the fundamental concept of order and harmony that governed the universe and human society. Her influence permeated every aspect of life.
Above all, she personified the essential principle of Ma’at, which Egyptians strove to uphold through their actions. This concept was a key emphasis in their culture, from the pharaoh’s rule to the daily lives of common people. Egyptians believed that maintaining Ma’at ensured the world continued to function properly, preventing chaos and disorder. She was one of the most significant goddesses because she embodied this notion of balance and harmony, without which the world would cease to exist.