How Were They Built? (The Great Debate)

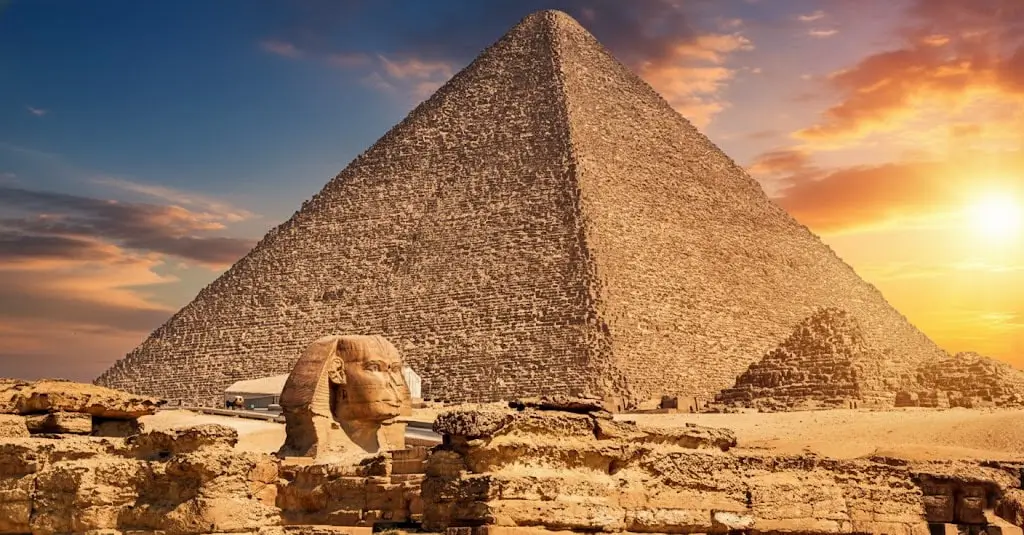
Knowing why they built them, we now face the biggest question: how? How did a Bronze Age civilization move and lift millions of 2.5-ton blocks with such perfect precision?
The Workforce: Who Really Built the Pyramids?
First, we must debunk the most persistent myth: it was not slaves. This idea comes from Hollywood films, not history.
The real evidence comes from archaeologists like Dr. Mark Lehner, who discovered the “Lost City” (Heit el-Ghurab) right at Giza. This was a massive, highly-organized city for the pyramid builders.
What they found there proves the builders were a rotating workforce of 10,000 to 20,000 skilled, paid, and well-fed Egyptian laborers. They uncovered huge bakeries, breweries, and fish processing areas, proving the workers ate a high-protein diet. They also found evidence of advanced medical care, like set bones. These workers were respected artisans and farmers who worked on the pyramids during the Nile’s annual flood.
The Great Ramp Debate
The central mystery remains how they lifted the blocks. This is the core of all pyramid construction theories. Most experts agree they used ramps, but they debate the type. Did they use a massive, long straight ramp? Or a “zig-zag” ramp on one side? Perhaps a spiral ramp that wrapped around the pyramid as it grew? Or did they use a more recent and compelling theory: an internal ramp that spiraled up inside the pyramid’s body? This is a massive topic in itself, involving complex physics and engineering.
Go Deeper: How did they lift 80-ton granite blocks? For a full analysis of ramp theories and the internal ramp hypothesis, read our Definitive Guide to Pyramid Construction Theories.
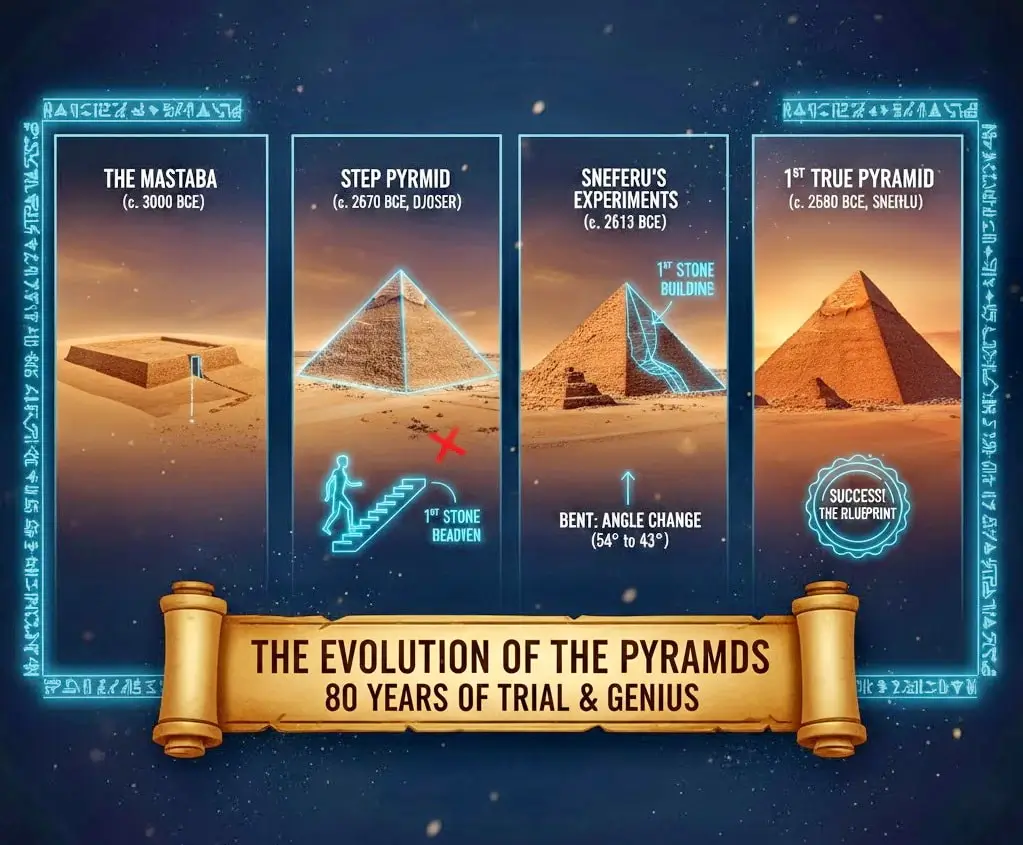
The Twilight of the Pyramid Builders

After the immense cost and effort of the Giza plateau, the era of colossal Egyptian pyramids began to wane. Pharaohs continued to build them, but their focus, materials, and scale changed dramatically.
5th & 6th Dynasties: The “Pyramid Texts”
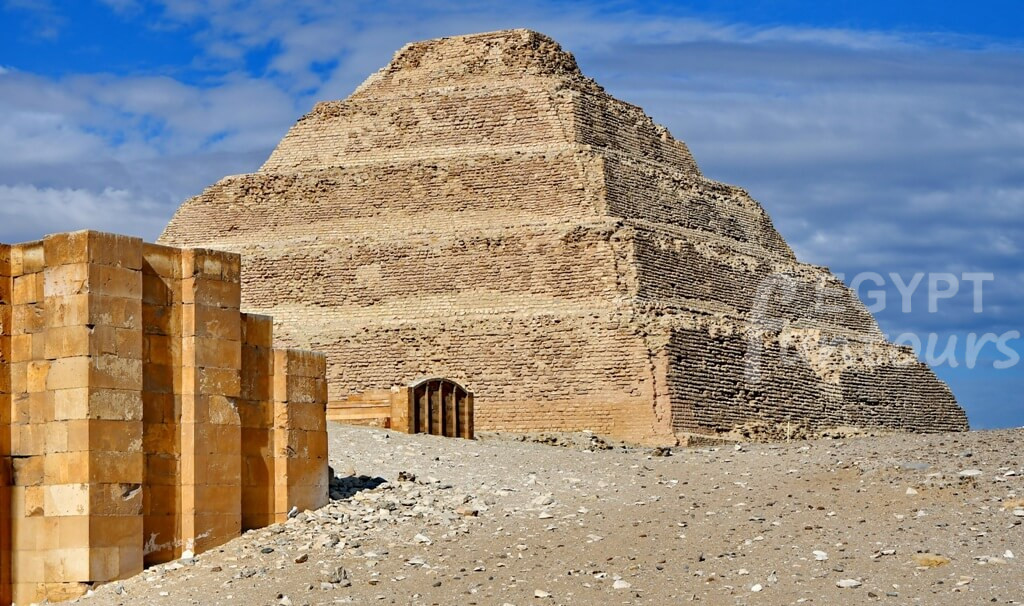
Pharaohs of the 5th and 6th Dynasties, like Unas at Saqqara, kept building pyramids. However, these monuments were much smaller. They used a core of rubble, which means many have crumbled into hills of debris.
But they introduced a revolutionary new innovation. The focus moved inside. For the first time, they covered the walls of the burial chamber with hundreds of hieroglyphic spells. We call these the Pyramid Texts. These spells were a divine “guidebook” to help the pharaoh’s soul overcome dangers and successfully reach the afterlife. This is the origin of the famous Book of the Dead.
The Middle Kingdom & Beyond
Centuries later, pharaohs of the Middle Kingdom tried to “revive” pyramid building. But they built these new Egyptian pyramids (at sites like Hawara and Dahshur) mostly from mud-brick with a stone casing.
As a result, they have not survived the test of time. Today, they look like simple, eroded mounds of earth. This decline reinforces that the true, stone-mountain “Pyramid Age” truly belongs to the Old Kingdom.